Video surveillance and analytics











Smart video surveillance for large areas
New level of control and analysis with revolutionary Panomera® technology
The new standard in video analytics
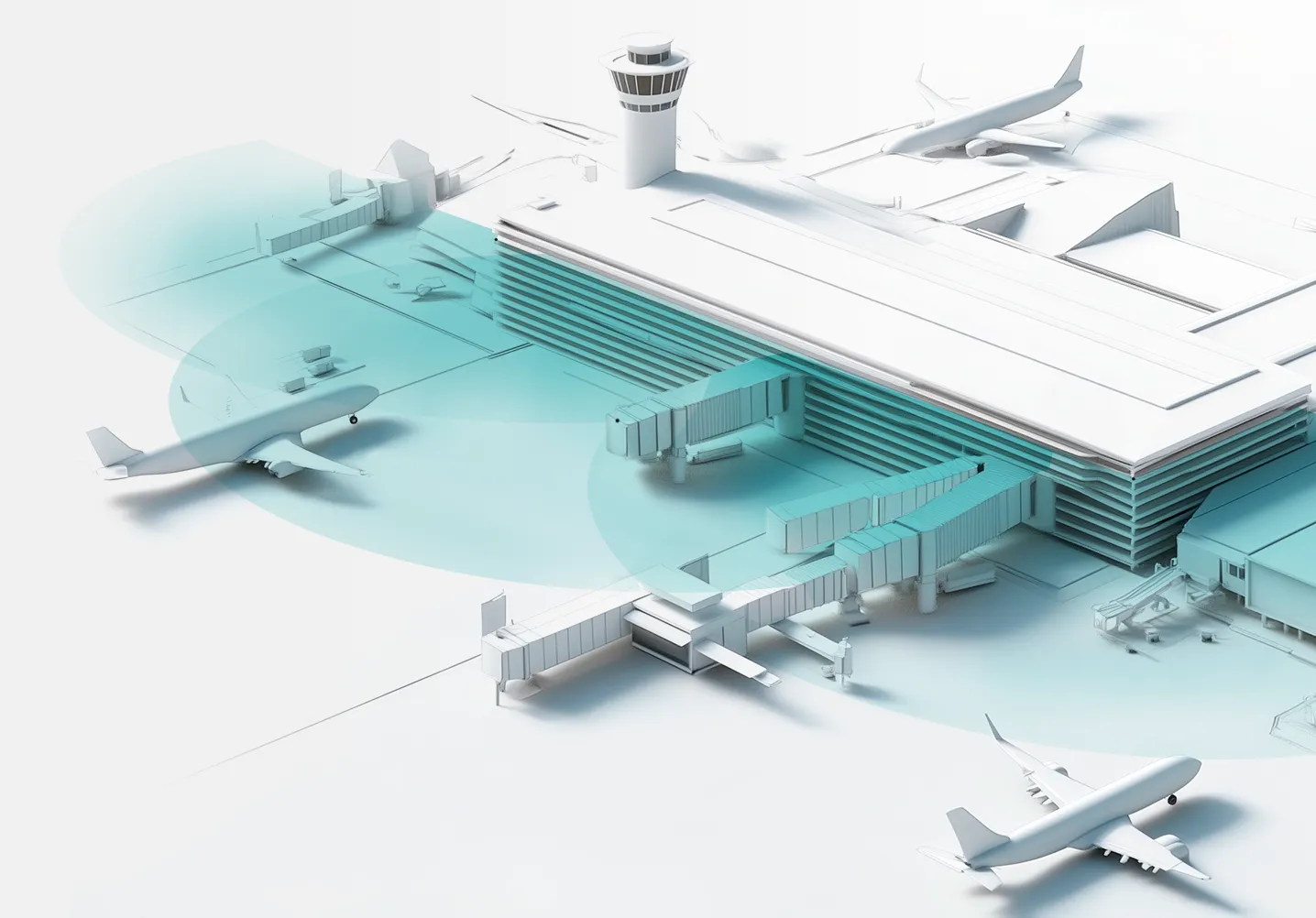
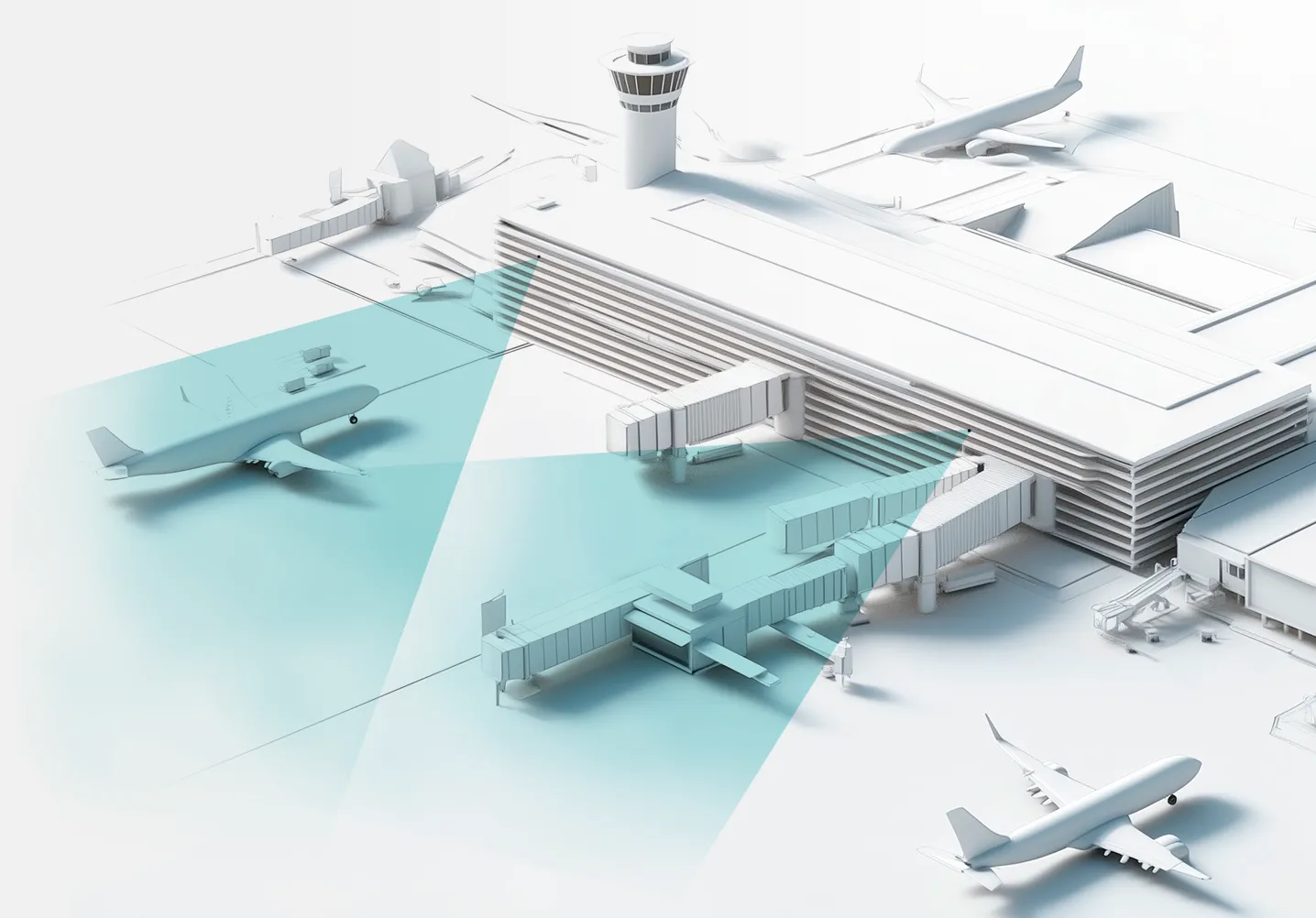
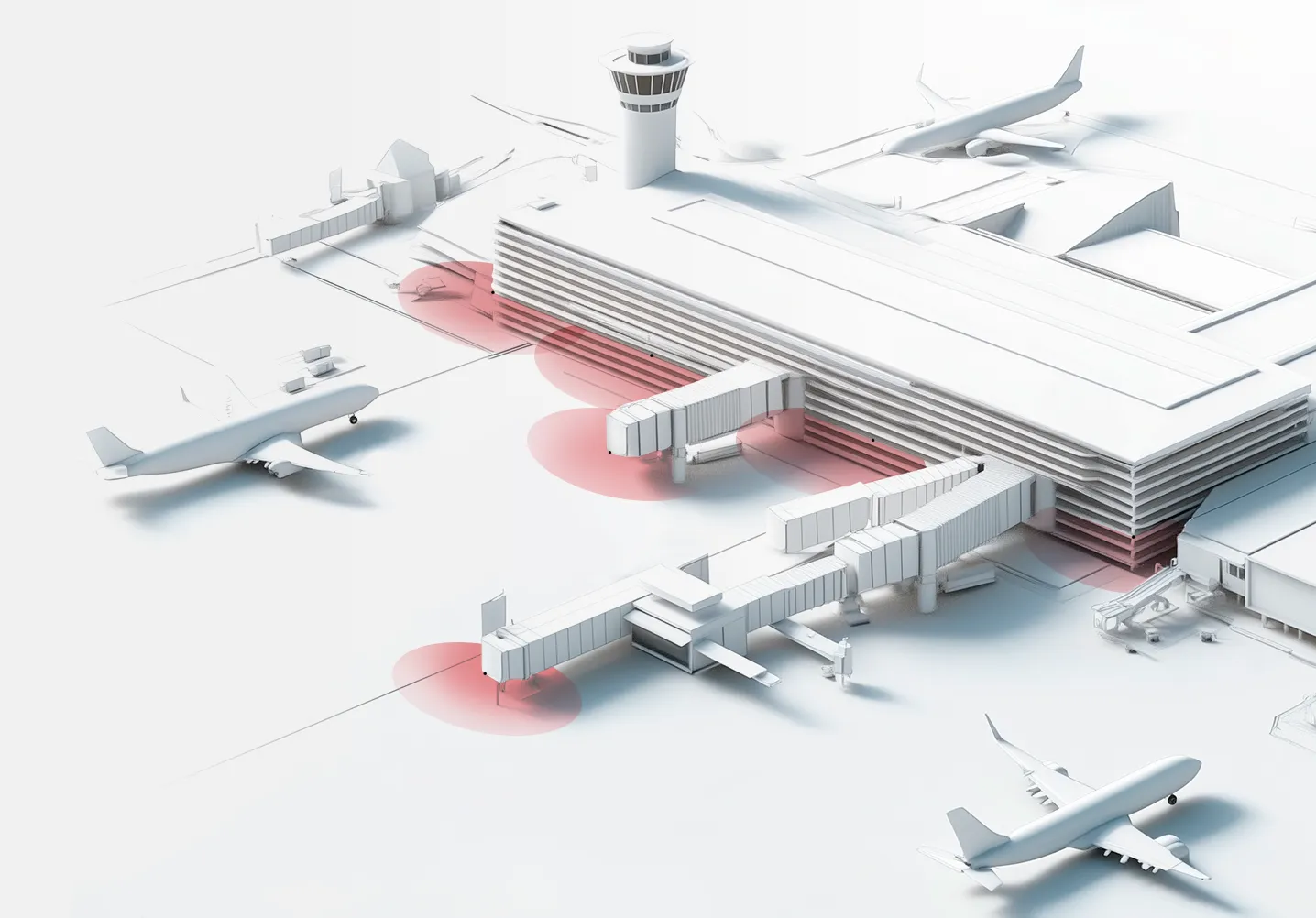
With just one Panomera® camera, you can monitor a vast area with incredible detail.
The video surveillance system reduces resources and infrastructure: 24 times fewer cameras are required, one camera covers up to 3,000 sq.m at a level of detail over 250 pixels per meter (identification), 90% less infrastructure, and up to 12,000 sq.m per camera at a level over 125 pixels per meter (recognition).



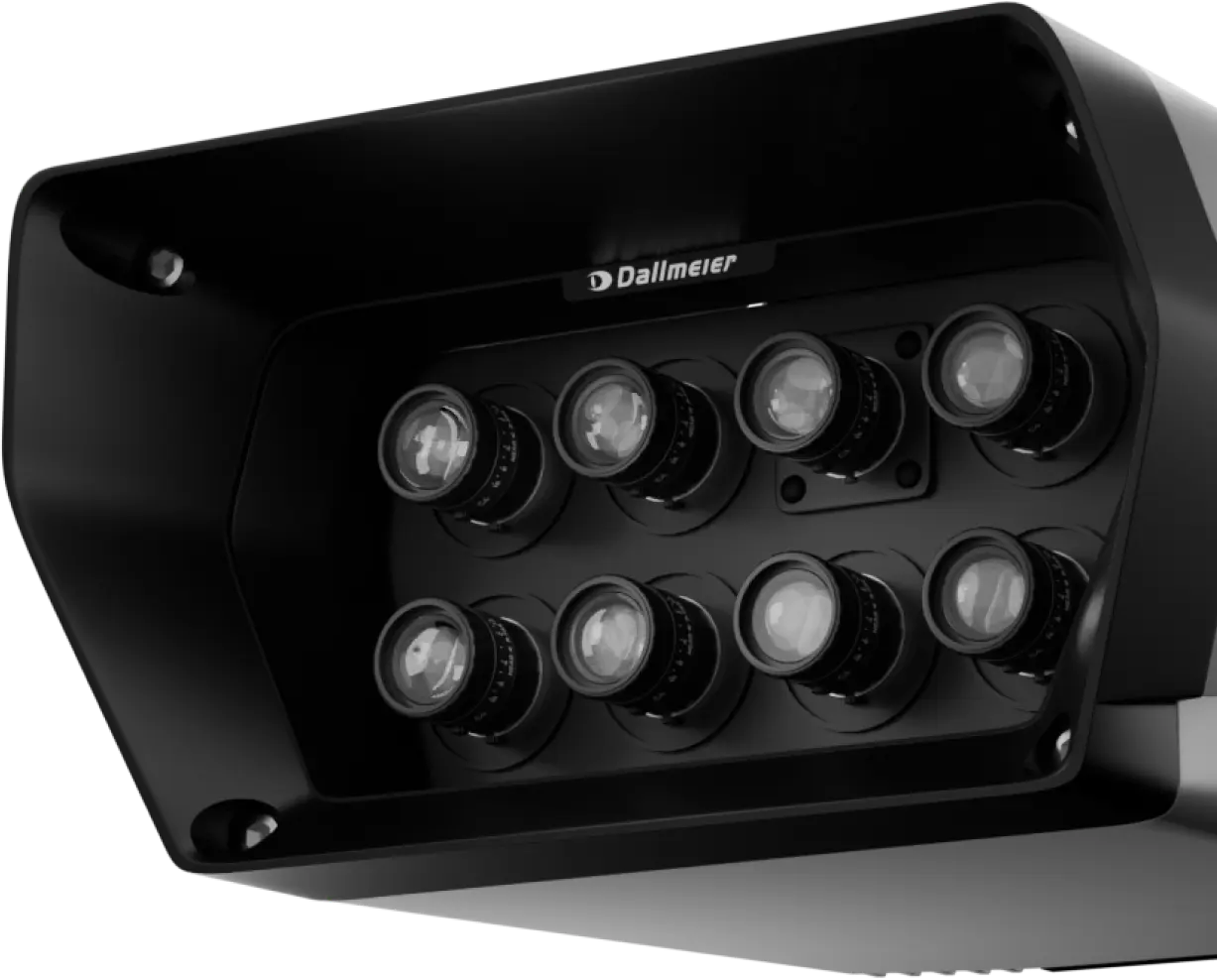
8 lenses for better detail

The highest resolution in real-time
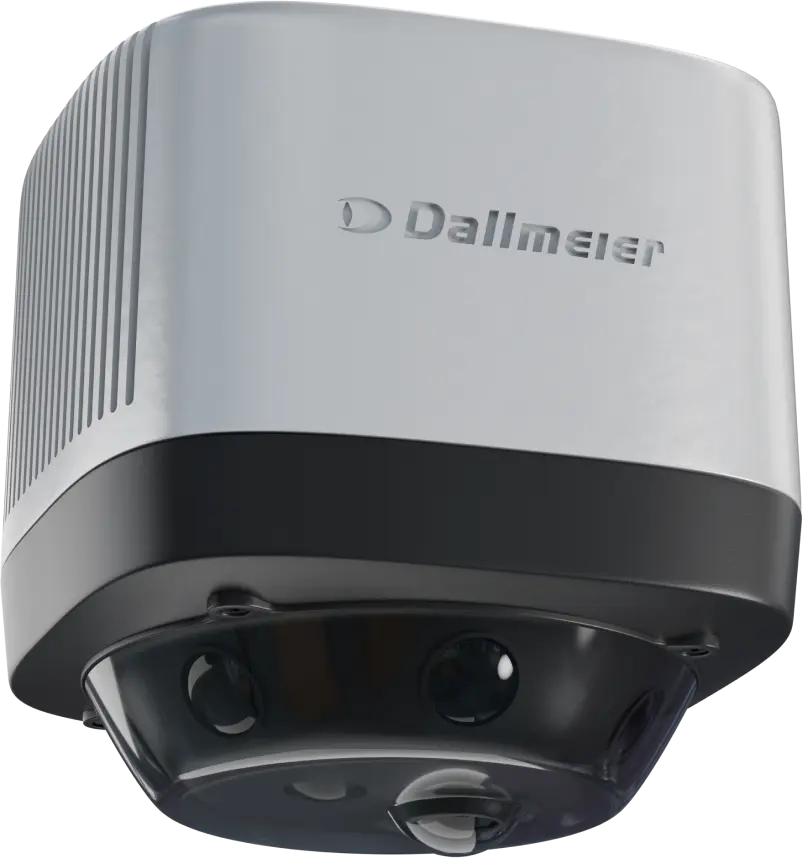


The widest possible visual angle
Maximum scope
The Panomera® multifocal sensor system uses innovative lenses and sensors technology to ensure consistent image quality even in the far distance. This enables Panomera® to achieve uniform resolution throughout the entire image area, so that distant objects have the same high resolution as foreground objects. In the Panomera® W the lenses of the multifocal sensor are arranged radially to capture a complete 360° panorama in a holistic view.
Therefore Panomera® significantly outperforms conventional HD and megapixel cameras.


Panomera S-Series
Multifocal sensor technology
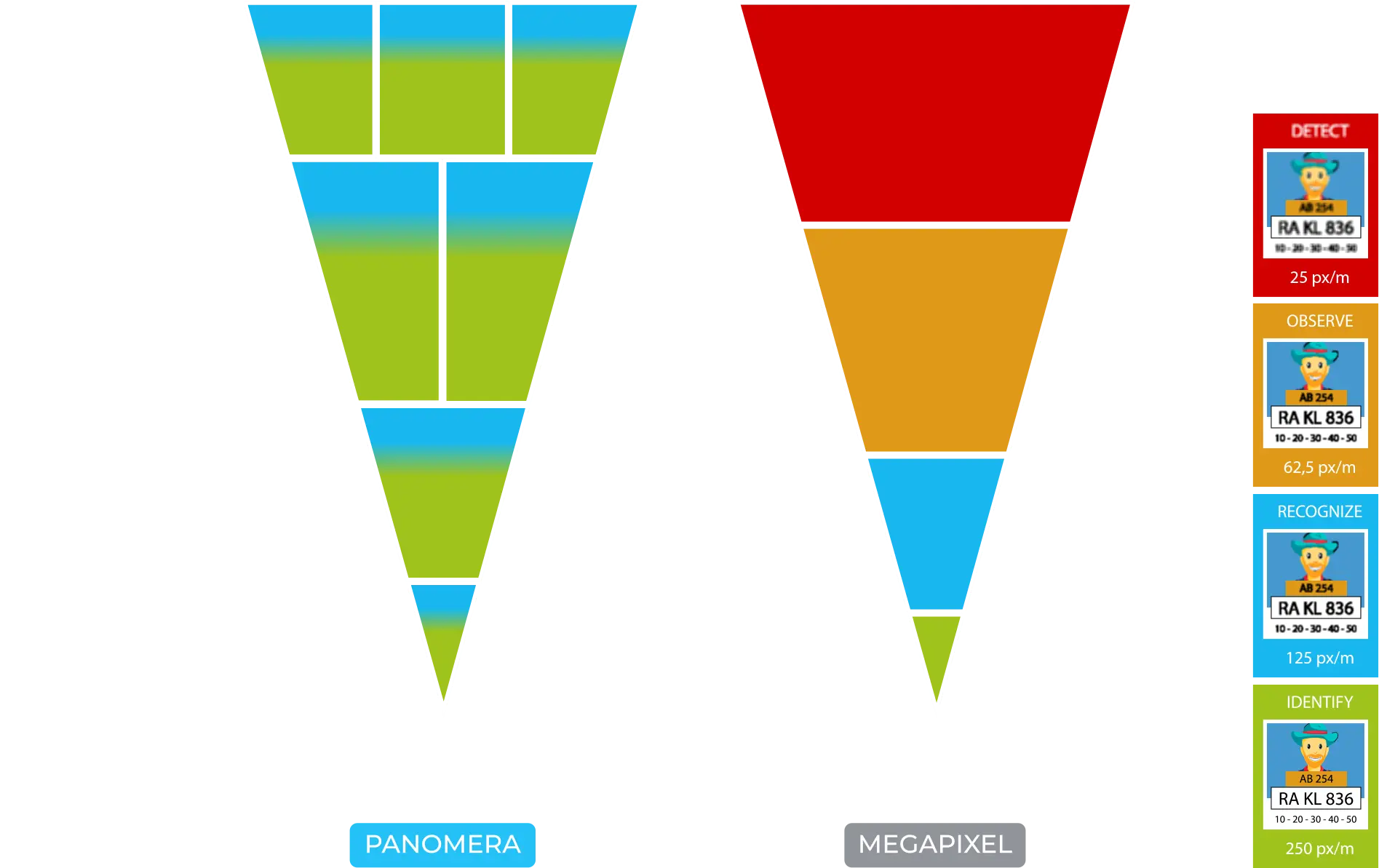
DIN EN 62676-4
The DIN EN 62676-4 standard specifies pixel density requirements depending on the application. For example, 125 pixels per meter are required to recognise familiar people or criminals while 250 pixels per meter are necessary to identify unfamiliar faces. Typically a minimum density of 62.5 pixels per meter is required to analyse and distinguish objects, depending on their size.
Panomera® technology offers high efficiency requiring a minimum number of cameras to cover a much larger area compared to conventional solutions.
Why Panomera®?
With Panomera® cameras customers can monitor large areas or long distances using less equipment compared to conventional solutions.
Panomera® is a virtual combination of multiple PTZ cameras and megapixel devices. Thus large areas or distances can be monitored using fewer cameras, which ensures maximum efficiency. This is beneficial for all participants in the process — from designers and installers to security system operators, managers and decision makers.

Beyond the image



Data analytics with Artificial Intelligence
Innovative object recognition system based on artificial intelligence
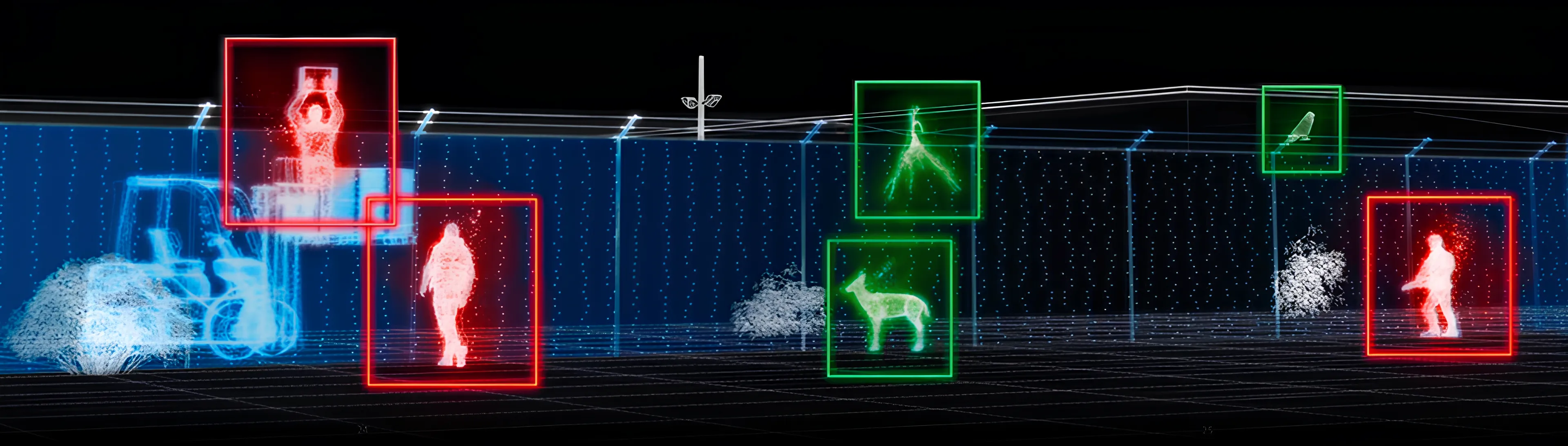
Classification of objects by type
Precise identification of people, cars, large vehicles and even animals.
Intelligent scenarios
Intrusion detection, crossing of virtual lines, analysing queues and counting objects in specified zones.
Misidentifying minimization
Neural networks filter out unnecessary data such as background movements and focus on significant events.

